Menu
CALL US: 0409 980 776
Patio installer rates in Perth differ from company to company. The main difference in patio installation rates in Perth is predominantly due to business size. The business size often correlates with the level of experience, quality of service and quality of product provided; the larger the company, the larger the price and often the larger the quality of product and service. This article aims to give some advice about patio companies in general so that you can feel informed when choosing your preferred patio builder.
Company size and patio installation rates are tied. A big patio company will likely have a large office, multiple employees, multiple contractor teams and a large advertising budget. As overheads grow, the need for a higher price is inescapable. A big patio company will often have been in the industry for a long time, do quality work and honour their warranties.
Note: A large, cheap company is likely skimping on labour, materials and service.
A small patio company or solo tradesman will often be the cheapest as they lack the overheads of a large company. These styles of business can be touch and go in terms of service, experience and product quality. They likely haven’t been in the industry all that long and may close up shop, making after-sales service and honouring of warranty potentially troublesome.
Note: There is not a trade certificate for patio construction. Just because someone is a carpenter or sheet metal worker or roof plumber does not mean they can design and build a good patio. Always ask to see examples of previous work.
Our recommendation is to go with a midrange patio company who has been operating for at least 5 years. These companies benefit from lower overheads but also have a wealth of knowledge in design and installation. The small business mentality also ties their reputation to their business and they provide good service and good product quality.
| Colorbond Gable Patio | $300-480m2 |
| Colorbond Flat Patio | $200-300m2 |
| Insulated Gable Patio | $500-650m2 |
| Insulated Flat Patio | $450-550m2 |
| Sunroof Patio | $1350-1650m2 |

Venture Outdoor provide you with a range of patio and outdoor renovation solutions that can be tailored to match your needs.
Venture Outdoor provide you with everything you need to create the outdoor entertainment area you’ve been dreaming of.
© 2023 Engineering On Demand
Before erecting a patio, particularly in coastal regions in Northern Australia it is important to consider a range of factors: Region (Figure 1.0), Terrain Category (Figure 2.0), Shielding Factor (Figure 4.0), and Topographic Classification (Table 2.0).
For permissible gust wind speed refer to table (1.0).
This considers these four variables in accordance with the Australian Standard AS/NZS1170.2:2011.

| Wind Classification | Gust Wind Speed meters per second | |
|---|---|---|
| Regions A & B | Regions C & D | |
| N1 (Non-Cyclonic) | N/A | W28 |
| N2 (Non-Cyclonic) | N/A | W33 |
| N3 (Non-Cyclonic) | C1 (Cyclonic) | W41 |
| N4 (Non-Cyclonic) | C2 (Cyclonic) | W50 |
| N5 (Non-Cyclonic) | C3 (Cyclonic) | W60 |
| N6 (Non-Cyclonic) | C4 (Cyclonic) | W70 |
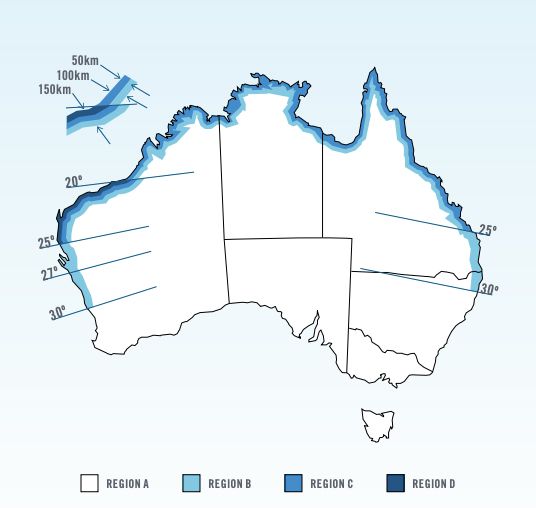
| Topographic Classification | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Terrain Category | T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | ||||||||
| FS | PS | NS | FS | PS | NS | FS | PS | NS | FS | PS | NS | ||
| A | 1 | N2 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N4 | N4 | N3 | N4 | N4 |
| 1.5 | N2 | N2 | N3 | N2 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N4 | N3 | N4 | N4 | |
| 2 | N1 | N2 | N2 | N2 | N3 | N3 | N2 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N4 | |
| 2.5 | N1 | N2 | N2 | N2 | N2 | N3 | N2 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | |
| 3 | N1 | N1 | N2 | N1 | N2 | N2 | N2 | N3 | N3 | N2 | N3 | N3 | |
| B | 1 | N3 | N4 | N4 | N4 | N4 | N5 | N4 | N5 | N5 | N5 | N5 | N5 |
| 1.5 | N3 | N4 | N4 | N3 | N4 | N4 | N4 | N4 | N5 | N4 | N5 | N5 | |
| 2 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N4 | N4 | N4 | N4 | N4 | N4 | N4 | N5 | |
| 2.5 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N4 | N3 | N4 | N4 | N4 | N4 | N5 | |
| 3 | N2 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N3 | N4 | N4 | N3 | N4 | N4 | |
| C | 1 | C2 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C4 | C3 | C4 | C4 | C4 | C4 | N/A |
| 1.5 | C2 | C3 | C3 | C2 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C4 | C3 | C4 | C4 | |
| 2 | C2 | C2 | C2 | C2 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C4 | |
| 2.5 | C1 | C2 | C2 | C2 | C2 | C3 | C2 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C3 | N3 | |
| 3 | C1 | C2 | C2 | C2 | C2 | C2 | C2 | C3 | C3 | C2 | C3 | C3 | |
| D | 1 | C4 | C4 | N/A | C4 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 1.5 | C3 | C4 | C4 | C4 | C4 | N/A | C4 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| 2 | C3 | C3 | C4 | C3 | C4 | C4 | C4 | N/A | N/A | C4 | N/A | N/A | |
| 2.5 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C4 | C4 | C4 | C4 | N/A | C4 | N/A | N/A | |
| 3 | C2 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C3 | C4 | C3 | C4 | C4 | C4 | C4 | N/A | |
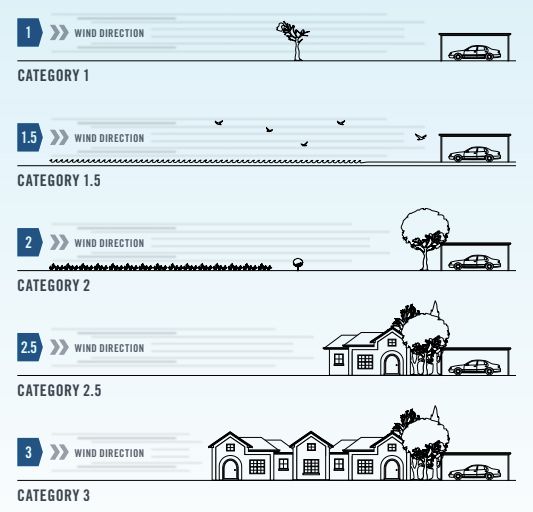
The windspeed impact upon a structure is further influenced by the terrain it flows over. Sparsely populated, clear land provides less wind resistance than undulating land with a greater density of trees and structures.
Category 1 Terrain which is open with few obstructions (trees or man made structures); may include enclosed water surfaces, flat, treeless and poorly grassed plains, rivers or lakes with no buildings, or enclosed bays less than 10km in the wind direction.
Category 1.5 Larger open water surfaces including coastal waters, large open bays on seas, oceans or lakes, and enclosed bays less than 10km in the wind direction.
Category 2 Open terrain, including grasslands with fewer than two obstructions (1.5 to 5m high) per hectare.
Category 2.5 Terrain with isolated obstructions such as outer urban areas with scattered houses and few trees.
Category 3 Terrain covered with numerous obstructions that are closely spaced, with heights between 3 and 10m. For example suburban housing.
The windspeed impact upon a structure is further influenced by the terrain it flows over. Sparsely populated, clear land provides less wind resistance than undulating land with a greater density of trees and structures.
Category 1 Terrain which is open with few obstructions (trees or man made structures); may include enclosed water surfaces, flat, treeless and poorly grassed plains, rivers or lakes with no buildings, or enclosed bays less than 10km in the wind direction.
Category 1.5 Larger open water surfaces including coastal waters, large open bays on seas, oceans or lakes, and enclosed bays less than 10km in the wind direction.
Category 2 Open terrain, including grasslands with fewer than two obstructions (1.5 to 5m high) per hectare.
Category 2.5 Terrain with isolated obstructions such as outer urban areas with scattered houses and few trees.
Category 3 Terrain covered with numerous obstructions that are closely spaced, with heights between 3 and 10m. For example suburban housing.
The windspeed impact upon a structure is further influenced by the terrain it flows over. Sparsely populated, clear land provides less wind resistance than undulating land with a greater density of trees and structures.
Category 1 Terrain which is open with few obstructions (trees or man made structures); may include enclosed water surfaces, flat, treeless and poorly grassed plains, rivers or lakes with no buildings, or enclosed bays less than 10km in the wind direction.
Category 1.5 Larger open water surfaces including coastal waters, large open bays on seas, oceans or lakes, and enclosed bays less than 10km in the wind direction.
Category 2 Open terrain, including grasslands with fewer than two obstructions (1.5 to 5m high) per hectare.
Category 2.5 Terrain with isolated obstructions such as outer urban areas with scattered houses and few trees.
Category 3 Terrain covered with numerous obstructions that are closely spaced, with heights between 3 and 10m. For example suburban housing.

| Terrain Category | Regions A, B, C, & D |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1.05 |
| 1.5 | 0.98 |
| 2 | 0.91 |
| 2.5 | 0.87 |
| 3 | 0.83 |
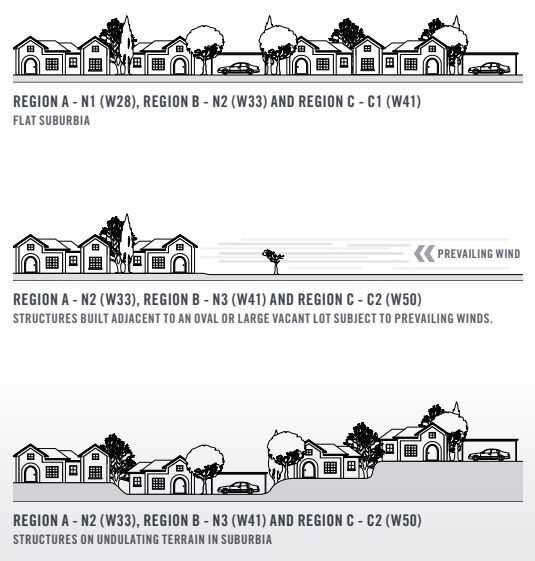
| Shielding Classifications | Factor |
|---|---|
| Full Shielding (FS) | 0.85 |
| Partial Shielding (PS) | 0.95 |
| No Shielding (NS) | 1.00 |
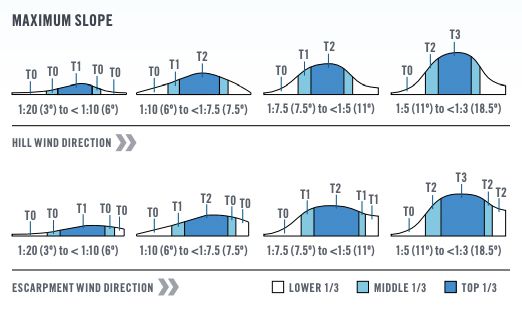
| Topographic Classifications | Factor |
|---|---|
| T0 | 1.00 |
| T1 | 1.10 |
| T2 | 1.20 |
| T3 | 1.30 |

Please Note: This document is provided as a design guide only. The information provided here is written in compliance with the requirements of AS/NZS1170.2:2011 and is classified in accordance with wind classifications allocated in AS4055:2012. Patio Engineering Australia does not accept any liability for any loss or damage that results from the misinterpretation of this design guide. When uncertain it is recommended to seek the advice of an independent engineer.